Pyromellitic Dianhydride/PMDA CAS 89-32-7
Product Name:Pyromellitic Dianhydride/PMDA
CAS:89-32-7
MF:C10H2O6
MW:218.19
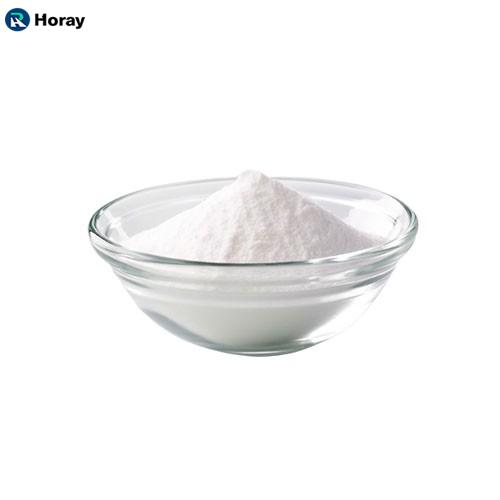
Appearance: White Powder or Crystal
Assay: 99%min
Package: 25kg/drum, 20kg/carton
Melting point: 286~288℃
[Typical Properties]
Easily soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide, acetone, soluble in chloroform, ether, n-hexane, and benzene.
[Specification]
Item | Standard |
Appearance | White crystal or powder |
Purity | ≥99.5% |
Melting point | 286~288℃ |
Free acid content | ≤0.5% |
[Usage]
*Mainly used for synthesizing polyimide, due to its excellent ultra-high heat resistance, acid and alkali resistance, outstanding mechanical properties, electrical properties, and dimensional stability, polyimide is widely used in high-tech fields such as aviation, aerospace, microelectronics, and atomic energy that require demanding material properties.
*Phthalic dianhydride (PMDA) is an important raw material for organic synthesis industry, as well as a basic raw material for the development of new chemical materials and high value-added fine chemical products. It is mainly used as a monomer for the production of polyimide, and can also be used as a curing agent for epoxy resin and crosslinking agent for polyester resin. It is used to manufacture phthalocyanine blue dye and some important derivatives, and has a wide range of applications. Phthalic anhydride, also known as phthalic anhydride, has a special molecular structure and can be used to manufacture materials with heat resistance, electrical insulation, and chemical resistance. Its main use is as a monomer for polyimide, synthesized with aromatic diamines to produce polyimide plastics. However, the purity requirement for phthalic anhydride is very high, reaching over 99%.
*It is also used to produce epoxy resin curing agents and plasticizers, urea formaldehyde resin stabilizers, phthalocyanine blue dyes, corrosion inhibitors, instant binders, electronic photography toners, etc.
[Storage]
Keep tightly closed.Store in dry and ventilated place.Keep away from fire,heat sources and oxidants.
INQUIRY
CATEGORIES
CONTACT US
Contact: sales@horayindustry.com
Phone: +86-13355429055
E-mail: info@horayindustry.com
Whatsapp:+86-13355429055
Add: No. 31 Longcheng Road,Shibei District,Qingdao City,Shandong Province,China.